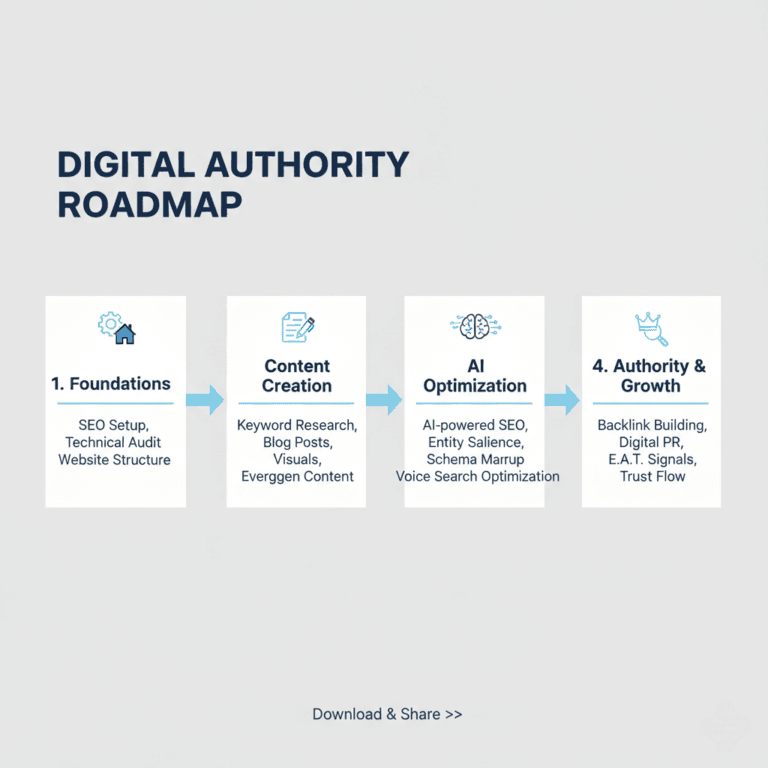
On-Page SEO: Free Tutorial, Checklist, & Best Techniques (2026)
On-page SEO is the practice of optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines. Unlike off-page SEO, which involves external signals like backlinks, on-page SEO refers to the elements you can control directly on your website, such as content, HTML tags, and site architecture.
In 2026, the definition has evolved. It is no longer just about placing keywords in specific locations. It is about creating a seamless user experience (UX) and demonstrating clear Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T).
Table of Contents
Google’s algorithms are smarter than ever. They prioritize pages that solve the user’s problem efficiently and comprehensively. This guide covers the essential strategies you need to master to ensure your content ranks at the top.
1. Master Search Intent and Content Depth
Before you optimize a single tag, you must optimize the concept. The foundation of modern on-page SEO is satisfying search intent. This means understanding why a user performed a search and delivering exactly what they need.
If a user searches for “best CRM software,” they want a comparison list, not a homepage for a single product. If they search “how to tie a tie,” they want a step-by-step video or guide, not the history of neckties.
Aligning Content with Intent Analyze the top ranking results for your target keyword. Are they blog posts, product pages, or videos? Your content format must match what Google is currently rewarding.
The E-E-A-T Factor Your content must demonstrate E-E-A-T. You can build this by:
- Showcasing Expertise: Use accurate industry terminology and cover the topic in depth.
- Demonstrating Experience: Share personal insights, data, or case studies that prove you know the subject firsthand.
- Building Trust: Cite credible sources and keep your content updated.
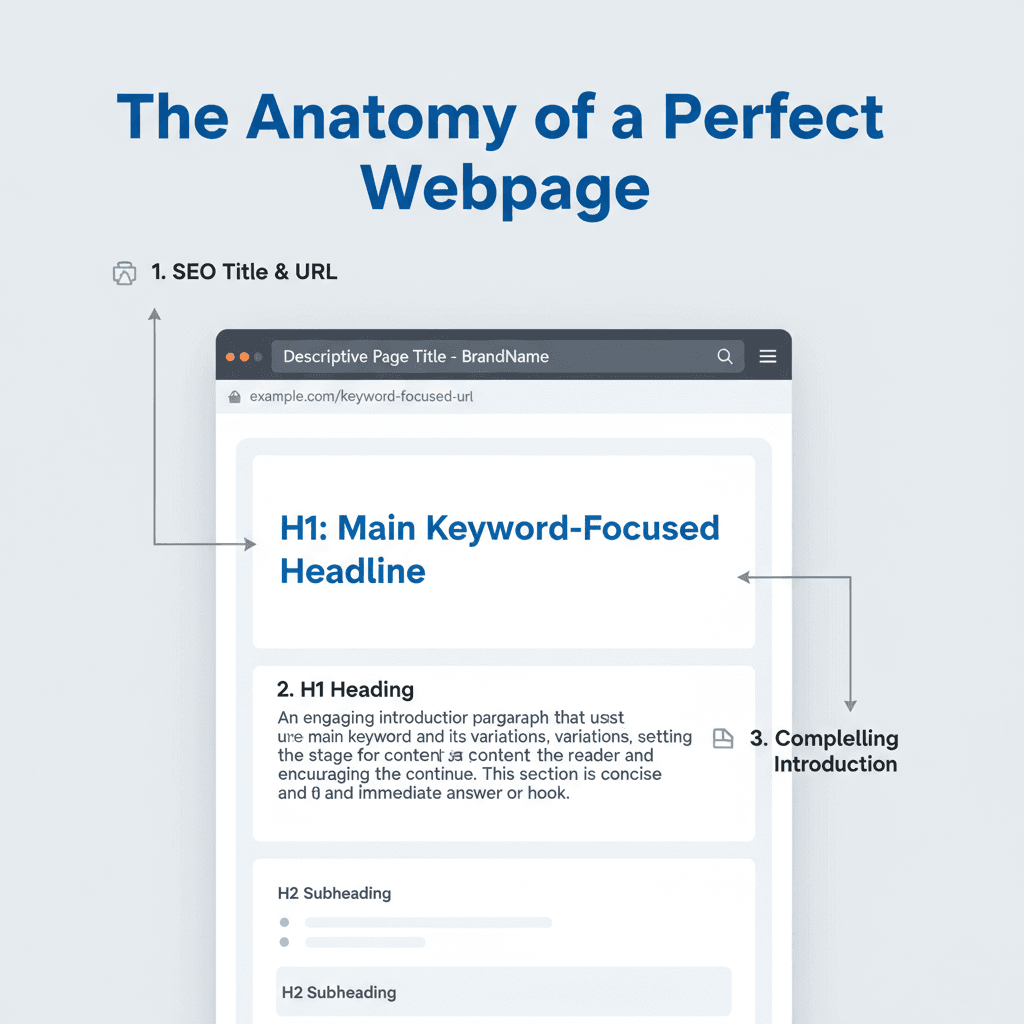
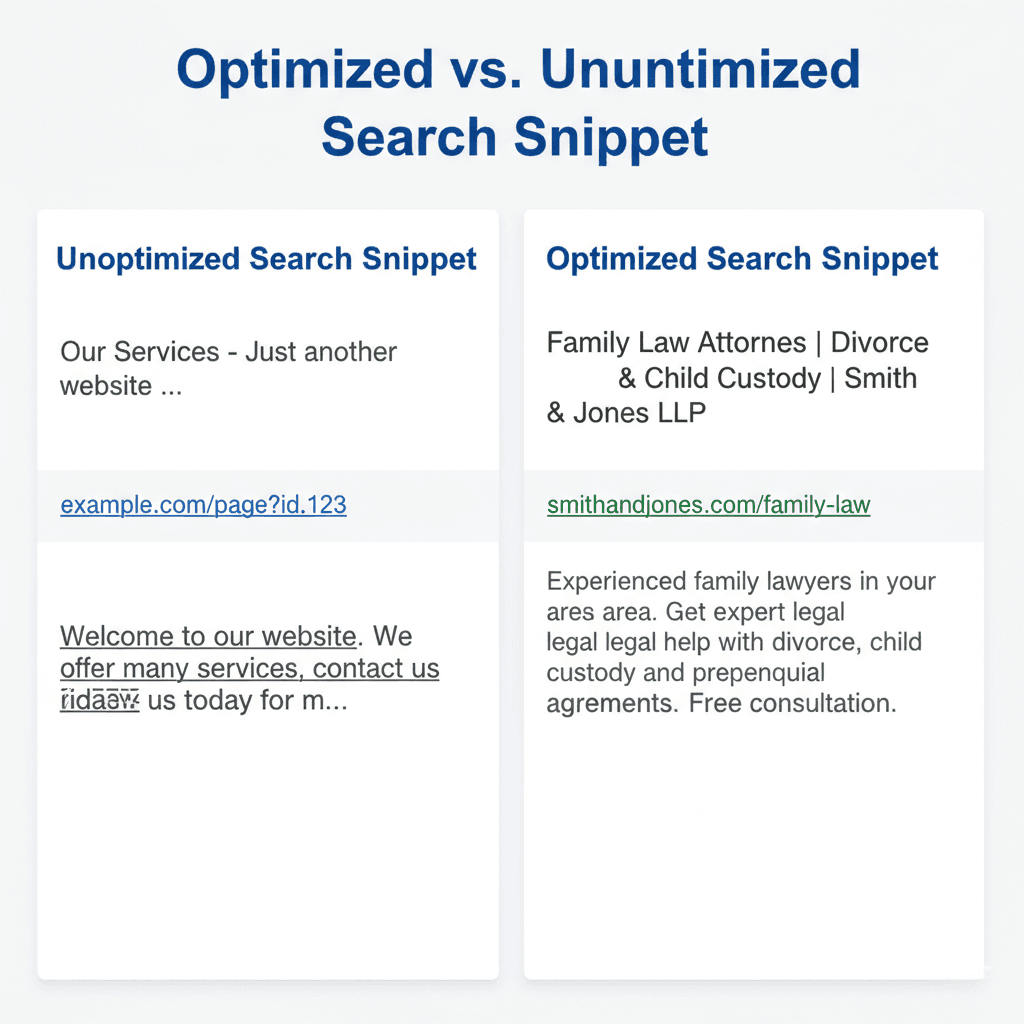
2. Optimize Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
Your title tag remains one of the most critical on-page ranking factors. It is the first thing a user sees in the search results.
Best Practices for Title Tags
- Front-Load the Keyword: Place your primary keyword (“On-Page SEO”) as close to the beginning of the title as possible.
- Keep it Under 60 Characters: This ensures the full title is visible in search results without being cut off.
- Add a Hook: Use words like “Guide,” “Checklist,” or the current year (2026) to increase the click-through rate (CTR).
Best Practices for Meta Descriptions While meta descriptions are not a direct ranking factor, they significantly influence CTR. Think of this as your ad copy.
- Include the Keyword: Google often bolds the search term in the description, which draws the eye.
- Focus on the Benefit: Tell the user what they will gain by clicking.
- Use Active Voice: Start with verbs like “Learn,” “Discover,” or “Master.”
3. URL Structure
A clean, descriptive URL helps both users and search engines understand what your page is about.
- Keep it Short: Shorter URLs tend to rank better.
- Include the Keyword: Use your focus keyword in the slug.
- Use Hyphens: Separate words with hyphens, never underscores.
- Avoid Dates: Do not include years or dates in the URL (e.g.,
/2026/01/post), as this makes it harder to update the content later.
Bad Example: seogrow.co/p=123 Good Example: seogrow.co/on-page-seo/
4. Heading Tags (H1, H2, H3)
Heading tags provide structure and hierarchy to your content. They help crawlers understand the main topics and subtopics of your page.
The H1 Tag You should have only one H1 tag per page. This is usually your page title. It must include your primary keyword and clearly state the topic of the page.
Subheadings (H2 and H3) Use H2 tags for your main sections and H3 tags for subsections. This breaks up the text and makes it scannable.
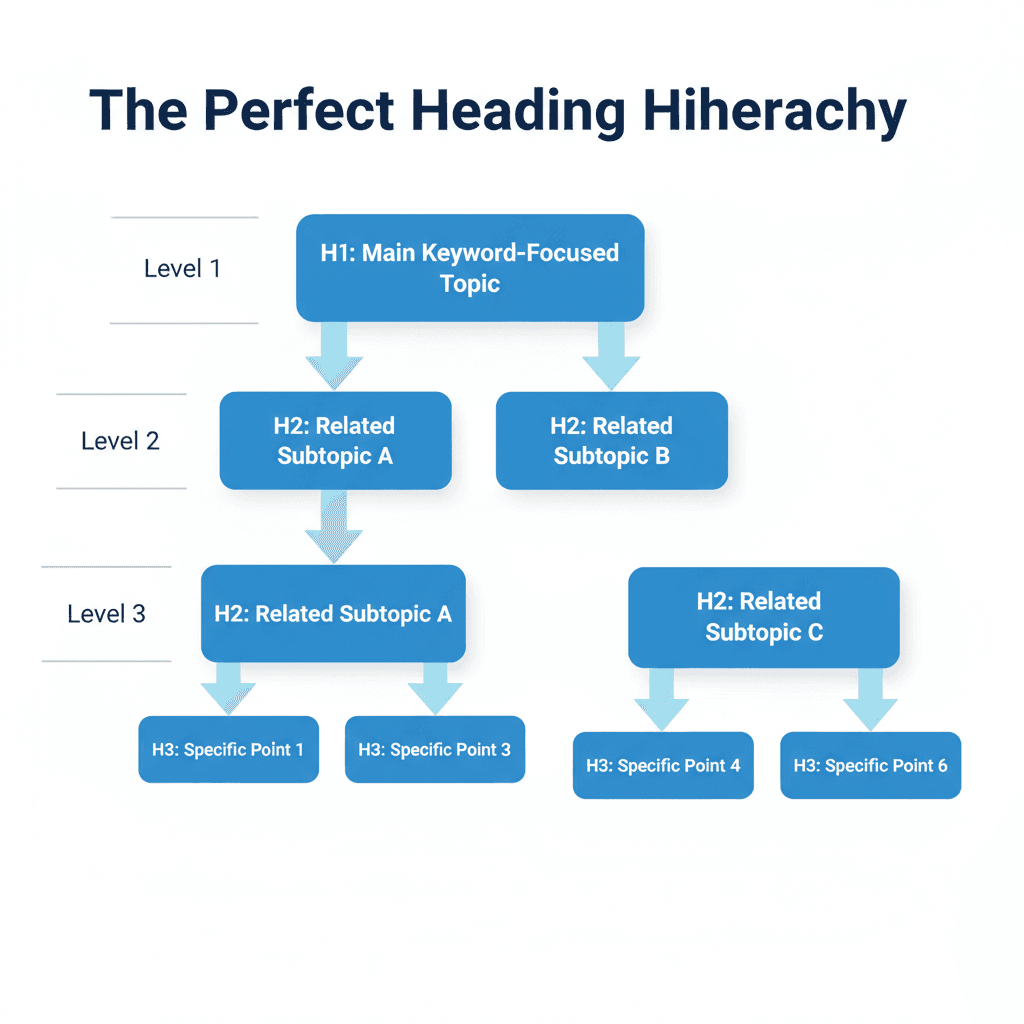
- Include Keywords: Incorporate secondary and long-tail keywords into your H2s naturally.
- Optimize for Featured Snippets: Frame H2s as questions (e.g., “What is On-Page SEO?”) to increase your chances of appearing in the “Position Zero” answer box.
5. Internal Linking Strategy
Internal linking is one of the most underrated on-page SEO tactics. By linking to other pages on your site, you pass authority (PageRank) and help Google discover new content.
Contextual Links Link to relevant articles within the body of your content. Use descriptive anchor text that tells the user and the search engine what the linked page is about. Avoid generic anchors like “click here.”
Topic Clusters Create “Hub” or “Pillar” pages that cover a broad topic, and link them to “Cluster” pages that explain specific details. For example, this guide is a hub that could link out to specific articles on “Title Tags” or “Image SEO.”
6. Image Optimization
Images enhance the user experience, but large files can slow down your site and hurt your rankings.
Alt Text Every image should have descriptive Alt Text. This text describes the image to screen readers for the visually impaired and helps search engines understand the image content. Include your target keyword if it is relevant to the image, but do not stuff keywords.
File Size and Format Compress your images before uploading them. Use modern, next-gen formats like WebP or AVIF for the best balance of quality and performance.
7. The On-Page SEO Checklist (2026)
Before you hit publish, run your page through this final checklist to ensure it is fully optimized.
- Keyword in Title Tag: Is the primary keyword near the front?
- Keyword in URL: Is the URL short and descriptive?
- Single H1 Tag: Does the page have exactly one H1 containing the keyword?
- Short Paragraphs: Is the content broken up into 2 to 3 line chunks for readability?
- Internal Links: Have you linked to 3 or more relevant pages on your site?
- External Links: Have you cited credible outside sources?
- Image Alt Text: Do all images have descriptive alt tags?
- Page Speed: Does the page load in under 2.5 seconds (LCP)?
- Mobile Friendly: Is the page responsive and easy to use on a phone?
| SEO Strategy Type | Key Findings & Trends | Statistical Benchmarks (2026) | Critical Content Structures | Measurement & Influence Metrics | Implementation Focus (Inferred) |
| Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) | Focuses on being cited as a trusted source in AI-generated responses (e.g., ChatGPT, Perplexity). AI-sourced visitors convert at a rate 12x higher than traditional search. | AI conversion rate: 27%; Average citations: 3-4 (ChatGPT), 13 (Perplexity); 70%+ proof density. | Answer-first architecture (direct answers in first 2-3 sentences), comparison tables, bulleted lists, and llms.txt files. | Share of Answer (SoA), Citation Rate, AI Presence Rate, and Brand Mention Frequency within LLMs. | Optimization for extractability by AI agents, original data assets (research/surveys), and mention-building on authority platforms. |
| Traditional SEO (Blue Links) | Evolving into a context-driven pillar based on intent-mapped content and E-E-A-T signals; serves as the foundational data layer for AI success. | Median Organic CTR: 1.25%; Median Avg Position: 33.44; Visitor-to-Lead Conversion Rate: 2.1%. | Long-form content (1,500-3,000 words), semantic topic clusters (pillar/cluster model), and non-branded internal linking. | Organic sessions, Keyword rankings (Top 3/10 distribution), and Domain Authority (DA). | Technical site health (crawlability, indexation), deep topical authority, and high-quality backlink acquisition. |
| Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) | Targets direct answers for voice assistants and featured snippets; prioritizes brevity and accuracy for “zero-click” utility. | Featured snippet appearance: 25% of results; Answer length: 30-50 words. | Question-based headings (H2/H3), FAQ schema markup, and concise Q&A pairs. | Featured snippet appearances, ‘People Also Ask’ (PAA) inclusions, and voice search results. | Conversational keyword targeting, structured data (Schema.org), and mobile-first responsiveness. |
| SaaS SEO (B2B Specific) | Primary growth mechanism for long sales cycles; 81% of buyers select vendors before direct contact. High ROI compared to paid channels. | SaaS SEO ROI: 784%; Organic CAC: 40-60% lower than paid; Target LTV:CAC Ratio: 3:1 to 5:1. | Product-led content (calculators, templates), case studies (3.5% conversion), and integration pages. | Organic MRR/ARR, Trial-to-Paid Conversion Rate, and Brand Perception within LLMs. | Aligning content to ICP pain points, managing complex URL structures, and reducing JavaScript-induced latency. |

By following these guidelines, you ensure your content is technically sound, highly relevant, and ready to rank in the competitive 2026 landscape.
You may also want to read about: