AI SEO Mistakes: 7 Errors Killing Your Brand Visibility by 2026
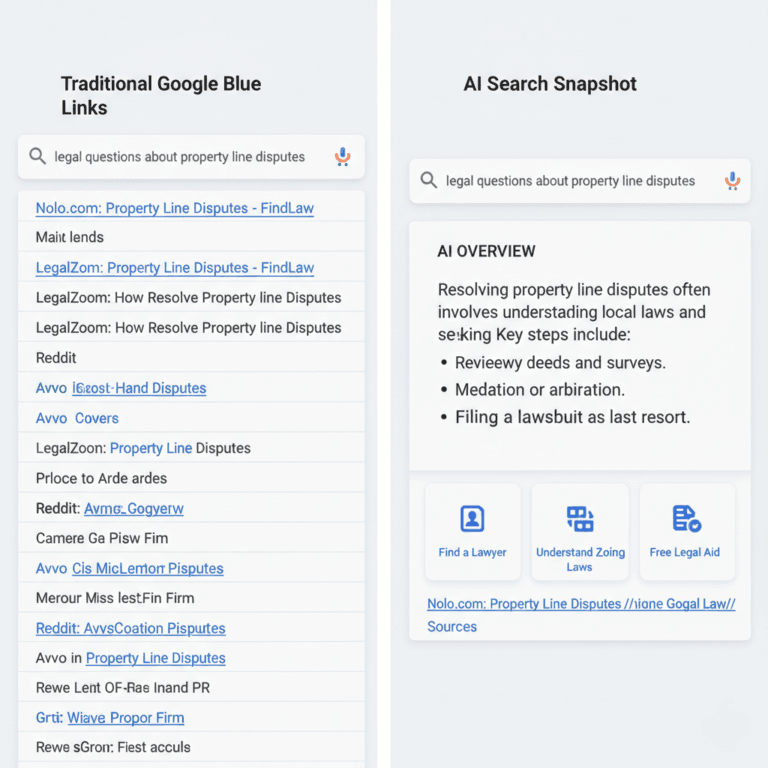
Search behavior undergoes a tectonic shift from navigation to synthesis. Digital marketing professionals now face the Zero-Click Crisis. SparkToro 2024 reports that only 37.4% of Google searches in the United States result in a click to the open web.
Google AI Overviews and ChatGPT provide immediate answers to complex queries. Traditional Click-Through Rate (CTR) suffers as Generative Engines synthesize content. Modern growth leaders struggle with Ghost Ranking: a state where sites rank well but AI models ignore them. Brands must pivot from keyword ranking to retrieval dominance to avoid common ai seo mistakes.
Table of Contents
Mistake 1: Optimizing for Keywords Instead of Micro-Intent
Legacy SEO strategies prioritize high-volume keywords. Targeting broad terms like “project management software” leads to total invisibility in 2026. AI models prioritize Micro-Intent: highly specific queries that address a precise user persona.
The Golden Formula in Action
- Entity: B2B SaaS Content
- Attribute: Lead Generation Growth
- Value: 400%
- Evidence: SaaS SEO and Conversion Strategies Study
Search algorithms prefer specificity to deliver grounded answers. Topic Hubs now replace single pillar pages. These interlinked ecosystems cover definitions: use cases: and localized nuances. Content must account for localized semantic relevance to capture conversational speech patterns.
Mistake 2: Ignoring GEO and AEO Optimization
Digital strategies often fail to distinguish between Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and Answer Engine Optimization (AEO). GEO focuses on securing citations in AI summaries. AEO ensures a brand remains the recommended choice in conversational interfaces.
What is the difference between Grounded and Model-Generated answers?
Grounded Answers rely on indexed sources in real-time. Technical SEO fundamentals like crawlability remain vital for these results. Model-Generated Answers stem from the pre-trained knowledge of the AI. Visibility in these results depends on long-term entity authority and training data representation.
Marketing agencies must optimize for both paths to capture the full discovery journey. The AI SEO Auditor identifies technical barriers blocking generative visibility.
Mistake 3: Treating Structured Data as Optional
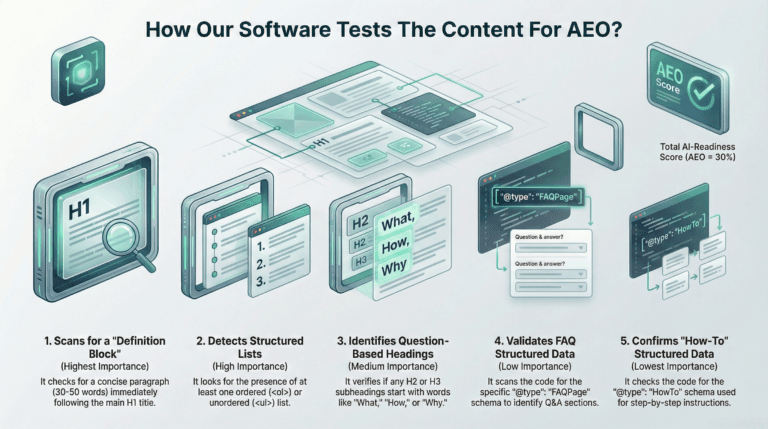
Schema Markup serves as a machine-readable requirement for modern search. AI shopping agents and overviews utilize structured data to minimize computational resources. Product: LocalBusiness: and FAQ schemas define entity boundaries for the engine.
JavaScript Rendering poses a significant technical barrier. Many modern websites rely on heavy client-side hydration. AI crawlers often skip content that requires JavaScript to render. If a bot cannot see the text in the initial HTML: the AI cannot cite the brand.
AI-Friendly Structure Checklist
- Answer Blocks: Provide direct answers in the first three lines under H2 headings.
- Machine-Readable Schema: Implement Article and FAQPage structures.
- Technical Accessibility: Deliver all extractable content without JS dependencies.
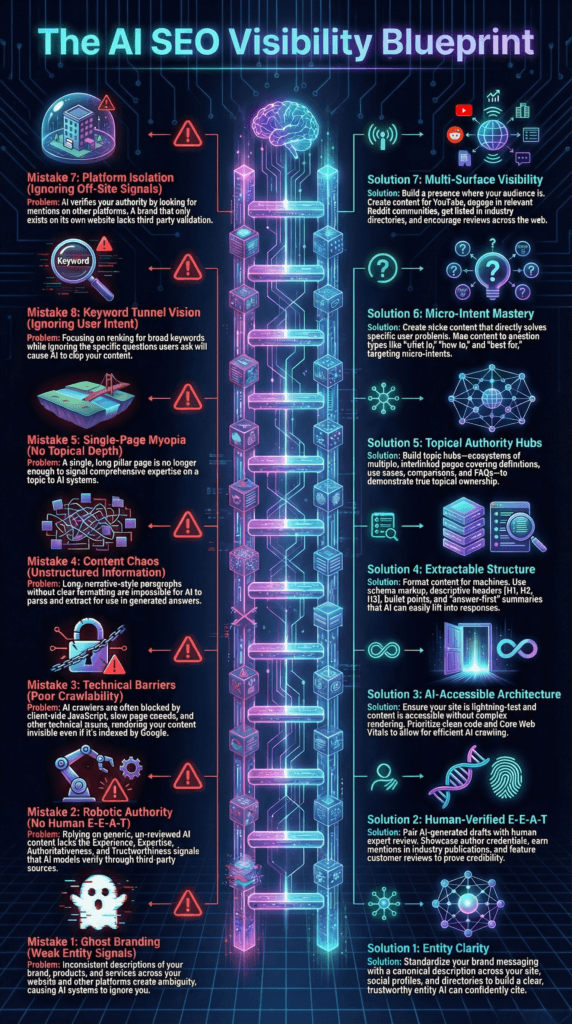
Mistake 4: The Ghost Brand Problem
AI systems verify authority through Third-Party Corroboration. A website remains a biased source when it is the only entity claiming expertise. This lack of external validation creates the Ghost Brand problem.
Entity Clarity requires social proof across Reddit: YouTube: and LinkedIn. Machine signals include star ratings and third-party reviews. AI bots use these signals to decide which brand to recommend with high confidence. Branded search volume serves as the new gold standard for SEO.
Mistake 5: Relying on Bland AI Content Without Human E-E-A-T
Generative content without human editing carries high strategic risk. Google E-E-A-T guidelines filter for scaled content abuse. Brands must move beyond “AI-only” workflows to avoid being flagged as generic noise.
The Content Framework for Human Authority
- Common: Foundational information found across all competitors.
- Unique: Industry insights that only specialists possess.
- New: Original data and case studies that do not exist elsewhere.
Original data prevents hallucinations and adds unique value. Content without this framework becomes a commodity that AI engines eventually filter out.
Mistake 6: Writing for Narrative Instead of Extractability
AI Overviews extract information rather than reading narratives. Long-form copy without clear structural markers fails the summarization test. Content must be extractable: meaning a bot finds a clear answer in a single block of text.
The Practical Rewrite Rule states that every keyword-focused sentence must become a question-focused answer. Information architecture transitions from pages to Topic Ecosystems. Every paragraph must serve as a potential standalone answer for an AI agent.
Mistake 7: Measuring Rankings Instead of Visibility Share
Traditional metrics like keyword rankings become vanity metrics in 2026. Success in the AI era requires a science of Controlled Experiments. Marketing managers must monitor the Brand Mention Share relative to competitors.
| Old SEO Metrics | Modern AI SEO Metrics |
| Keyword Rankings | Citations in AI Overviews |
| Click-Through Rate | Brand Mention Share |
| Backlink Count | Third-Party Corroboration |
| Total Clicks | Narrative Accuracy |
Citations in AI Overviews matter more than traditional blue links. The AI SEO Auditor evaluates structural gaps in brand visibility. Conduct a free audit to find the technical issues blocking your generative growth.
The New SEO Paradox
The SEO paradox of 2026 suggests that automation increases the need for human-centric data. AI redefines search as Multi-Surface Visibility. Success means the AI trusts the brand enough to recommend it as the definitive answer. Every brand must ask if an AI will mention them or a competitor today.
| AI SEO Mistake | Visibility Impact | Correction Strategy | Technical or Content Requirement | Recommended KPI | Success Signal (Inferred) |
| Ignoring AI Visibility (GEO/AEO) | Missing inclusions in AI Overviews and conversational tool recommendations like ChatGPT. | Adopt Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) specifically. | Structured data (schema), clear headers (H1-H3), and short paragraphs. | Citation share vs. competitors and inclusion rate in AI answers. | AI models perceive the brand as a primary source for definitive answers within the niche. |
| Lack of Third-Party Corroboration (Social Proof) | Models hesitate to cite claims that exist only on the brand’s own site, reducing trust scores. | Aggressively pursue reviews, media mentions, and Reddit/forum citations. | Review schema and mentions in authoritative industry publications. | Third-party citation volume and sentiment. | AI models treat the brand as a consensus-validated authority worth recommending. |
| Publishing Unstructured or Non-Extractable Content | AI Overviews cannot easily summarize or ‘lift’ fragments, favoring competitors with better structure. | Write for extraction: use ‘answer-first’ blocks and factual summaries to aid bot interpretation. | Bullet points, comparison tables, and FAQ schema. | Rich snippet/AI summary appearance rate. | Frequent appearance of brand content in featured answer modules and lists. |
| Inconsistent Brand Messaging Across Platforms | Lower AI confidence scores, leading to exclusion from citations or inaccurate brand descriptions. | Standardize brand definitions and product labels across website, socials, and directories. | One canonical positioning sentence and aligned schema entity fields. | Brand sentiment and narrative consistency score. | AI models generate a stable, accurate, and authoritative ‘brand entity’ profile across different platforms. |
| Technical AI Crawler Barriers | AI bots (which often do not render JS) cannot retrieve or index key content, leading to ‘invisible’ losses. | Ensure content is accessible to AI user agents without heavy client-side hydration. | Server-side rendering, clear robots.txt access, and clean HTML extraction paths. | AI crawler indexation rate and crawl success frequency. | High-speed retrieval and consistent data extraction by multiple LLM crawlers (GPTBot, etc.). |
| Over-Reliance on AI Output Without Quality Assurance | Risk of spreading ‘hallucinations’ or generic content that triggers Google spam/E-E-A-T penalties. | Keep a ‘human in the loop’ for editing, fact-checking, and adding unique expertise. | Fact-checking protocols and site scans for low-quality AI patterns. | E-E-A-T score audit and content originality rating. | Perceived high ‘Expertise’ and ‘Trustworthiness’ by search evaluators and algorithms. |
| Treating AI Search Solely as a Performance Channel | Setting unrealistic expectations for clicks/revenue while missing brand credibility gains. | Establish dual metrics for both branding visibility and assisted conversions. | First-touch attribution models and assisted-conversion tracking. | Share of Voice (SOV), branded search volume, and assisted revenue. | Increased brand recall and trust signals that shorten the customer decision journey. |
You may also want to read about: